
Documentation→Reference→Layers→Layer Types
Basic Types
 |
The layer type defines how the layer looks, be it a color, a cubemap or a procedurally generated texture. |
 Color ColorJust a plain color. Color - The color. Note: The mapping does not matter for this type. | |||
 Previous PreviousThe current color, defined by the previous layers. Note: This allows you to alter all the layers above. Currently you are unable to blur or pixelate previous layers. | |||
 Literal LiteralThe mapping's value. Note: - This uses the mapping's value. For example, with UVs the red is the X (0-1), and the Y is the green (0-1). |
|||
|
Resource Types | |||
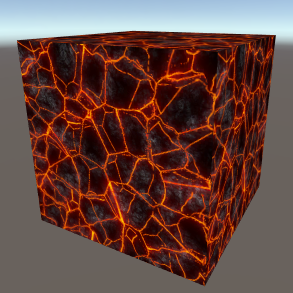 Texture TextureA 2D texture. Texture - The texture. | |||
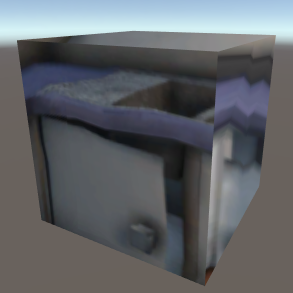 Cubemap CubemapA 3D cubemap, used commonly for reflections. Cubemap - The cubemap. |
|||
 Vertex Colors Vertex ColorsThe vertex colors. Note: The mapping does not matter for this type. Note: You can assign vertex colors within your 3d modelling program. The image to the side has a model whose vertex colors are baked AO. | |||
 Data DataVarious bits of data that could be useful. Data - The piece of data chosen (Light Direction, Light Attenuation, Light NdotL, Light Color, View Direction, Parallax Depth, Parallax Shadowing, the Layer Channels (Albedo, Normal etc).) | |||
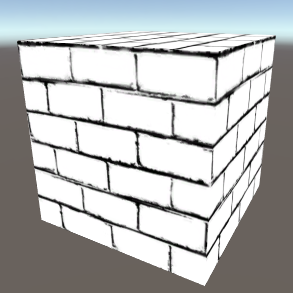 Mask MaskDisplays an RGBA mask created in the Masks tab. Mask - The mask to display (RGBA masks only). Note: The mapping does not matter for this type. Note: The image to the side is displaying a mask that contains a texture type layer. |
|||
|
Procedural Types | |||
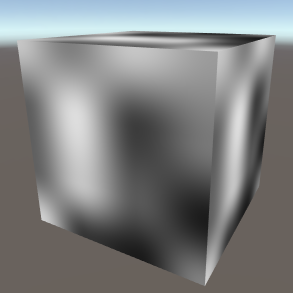 Cloud CloudProcedurally generated blocky noise. Kind of slow and looks the worst, not recommended unless a specific effect is needed. Dimensions - The number of dimensions the noise occupies (important when using 3D mapping types or when offsetting the Z map). | |||
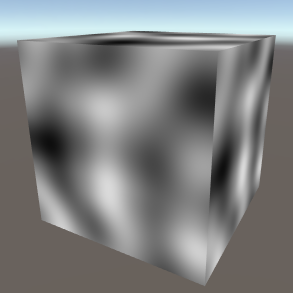 Perlin PerlinPerlin Noise, smoothly flowing and non repeating. Dimensions - The number of dimensions the noise occupies (important when using 3D mapping types or when offsetting the Z map). |
|||
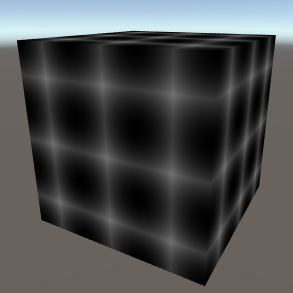 Cell CellCell based noise, can be used to create interested cellular or gridular effects. Dimensions - The number of dimensions the noise occupies (important when using 3D mapping types or when offsetting the Z map). Jitter - The amount the cells can be offset and warped. | |||
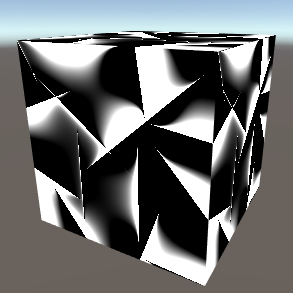 Cubist CubistOne of the stranger noise types, Cubist noise creates sharp corners and a discontinous look. Dimensions - The number of dimensions the noise occupies (important when using 3D mapping types or when offsetting the Z map). Fill/Edge - The weights used to determine how skinny or large the bright parts are. |
|||
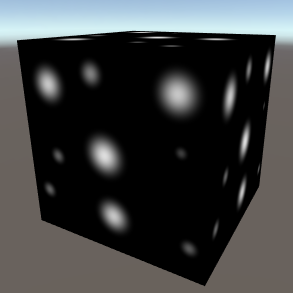 Dot DotProcedurally generated dots. Dimensions - The number of dimensions the noise occupies (important when using 3D mapping types or when offsetting the Z map). Min/Max Size - The minimum and maximum size of the dots. Square - Whether the dots are square or circular. | |||
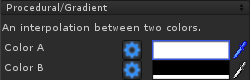
 Gradient GradientAn interpolation between two colors across the mapping. Color A/B - The colors to be interpolated/blended together. |
|||
|
Screen Types | |||
 Grab GrabLet's you access the Grab Pass, a pass that captures the screen, executing just before the rendering of the object with this shader. Note: in general you'll want to use the View mapping type to project the screen's image back onto the screen. | |||
 Depth DepthLet's you access the Depth Pass, a pass that captures the distance of the pixels on the screen from the camera. Note: in general you'll want to use the View mapping type to project the screen's image back onto the screen. |
|||
Copyright 2016 :) | Terms and Conditions!
